StudentShare


Our website is a unique platform where students can share their papers in a matter of giving an example of the work to be done. If you find papers
matching your topic, you may use them only as an example of work. This is 100% legal. You may not submit downloaded papers as your own, that is cheating. Also you
should remember, that this work was alredy submitted once by a student who originally wrote it.
Login
Create an Account
The service is 100% legal
- Home
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services
- Extra Tools
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us
✕
- Studentshare
- Subjects
- Environmental Studies
- Energy Sustainability Calculations
Free
Energy Sustainability Calculations - Case Study Example
Summary
The study "Energy Sustainability Calculations" focuses on the critical analysis of the calculations on CO2 Si for four major regions of the world, the European Union, United States, People’s Republic of China, India, and South Africa. All values to be used for the various regions are that of 2010…
Download full paper File format: .doc, available for editing
GRAB THE BEST PAPER98.2% of users find it useful
- Subject: Environmental Studies
- Type: Case Study
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 4 (1000 words)
- Downloads: 0
- Author: favian82
Extract of sample "Energy Sustainability Calculations"
Energy Sustainability The following calculations look at CO2 Si for four major regions of the world. The regions are the European Union, United s, People’s Republic of China, India and South Africa.
The general formula to be used is stated as follows:
Si = (P) x (GDP/P) x (E/GDP) x (CO2/E) – (CO2)sq
Where P = Population; GDP = Gross Domestic Product; E = Energy Consumption; CO2 = Carbon dioxide emission; (CO2)sq = carbon dioxide sequestered
It most be noted that the GDP and all other values to be used for the various regions is that of 2010. Below are the Si calculations for the given regions.
European Union
P = 501,000,000
GDP = 16,242,256
E = 158,000MJ (source: Earth Trends)
CO2 = 4,177,817 metric tones
Assumption (CO2)sq for all regions = 0
From the above, Si (EU) = (501,000,000) x (16,242,256/501,000,000) x (158,000/16,242,256) x (4,177,817/158,000) – (0)
Si (EU) = (501,000,000) x (0.03242) x (0.00973) x (26.44)
Si (EU) ≈4,178,Mtons
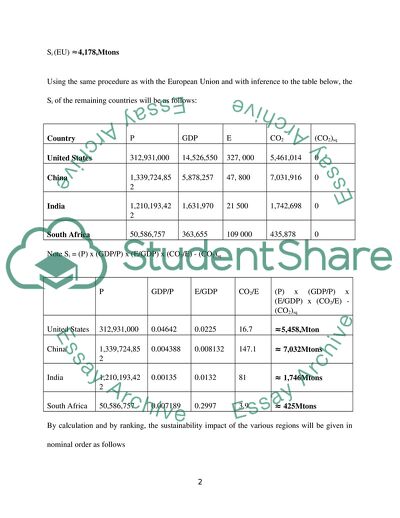
Using the same procedure as with the European Union and with inference to the table below, the Si of the remaining countries will be as follows:
Country
P
GDP
E
CO2
(CO2)sq
United States
312,931,000
14,526,550
327, 000
5,461,014
0
China
1,339,724,852
5,878,257
47, 800
7,031,916
0
India
1,210,193,422
1,631,970
21 500
1,742,698
0
South Africa
50,586,757
363,655
109 000
435,878
0
Note Si = (P) x (GDP/P) x (E/GDP) x (CO2/E) - (CO2)sq
P
GDP/P
E/GDP
CO2/E
(P) x (GDP/P) x (E/GDP) x (CO2/E) - (CO2)sq
United States
312,931,000
0.04642
0.0225
16.7
≈5,458,Mton
China
1,339,724,852
0.004388
0.008132
147.1
≈ 7,032Mtons
India
1,210,193,422
0.00135
0.0132
81
≈ 1,746Mtons
South Africa
50,586,757
0.007189
0.2997
3.9
≈ 425Mtons
By calculation and by ranking, the sustainability impact of the various regions will be given in nominal order as follows
Rank
Region
Si
1st
European Union
4,178,Mtons
2nd
China
7,032Mtons
3rd
United States
5,458,Mton
4th
India
1,746Mtons
5th
South Africa
425Mtons
Comparatively, the calculations made above do not differ so much from published and existing data. This is especially so as data was picked from only reliable and accepted academic sources such as the United Nations and European Union official websites. The little disparities seen however arise from inconsistency with years of comparison. For instance, in some publications, the year of population sample is compared with different years of GDP figures. When such situations arise, concluding values cannot be said to be very authentic.
Discussion
By and large, the data gathered above gives a lot of revelation about the present energy sustainability situation as it exists the world over. South Africa was strategically added to the list of countries considered to give a very fair global representation of the fight for energy sustainability. Among the revelations made from the calculations and findings is that the whole world seem to be loosing the battle on ensuring sustainable use of energy. It will be observed that energy sustainability concerns the prudent use of energy in such as way that not only the existing generation benefits but then generations unborn also benefit. However, the excessively higher values in carbon emission recorded in almost all countries used is highly unpardonable. Clearly, there is no way the generation of today can boast of any better legacy for generations to come if the trend continues. As noted by experts, carbon emission continues to damage the environment and brings about undeserving effects such as global warning and greenhouse effect. Until stiffer steps are taken towards the canker, no one can actually boast of energy sustainability as of now.
One strong solution to the problem lamented on energy sustainability in the above paragraph clearly rests with the alternative use of sources of energy. By alternative use of energy sources, reference is being made to those sources of energy that does not either produce any form of carbon emissions or highly reduced form of carbon emission. Some of the suggested alternative sources of energy that can be mentioned include solar energy, thermal energy and hydro energy. In other words, it would do the world a lot of good if a lot of dependence was done on renewable energy sources. Knowing that the three major pillars of sustainability are the economy, society and the environment, it can be argued beyond doubt that if renewable sources of energy are resorted to, all three aspects of sustainability will duly be satisfied. For instance society keeps expanding with increasing population trend. Meanwhile, renewable sources of energy are the commonest around us. This means that if we resort to renewable sources of energy, society can be assured of constant supply of energy for daily purposes. As far the economy is concerned, the economy has nothing to lose if renewable energy is made the prime source of energy supply for the world. Indeed as much as some would argue that most countries will loss their source of income through exportation of non-renewable energy sources, it would also be true to say that a lot more countries would have expenditures to save rather than to trade in energy sources since renewable energy sources are found almost anywhere in this world. For the environment, it would be the greatest benefactor. Indeed, if 25% of all energy comes from renewable sources, there would be close to 25% cut in carbon emission and the same holds for any percentage of renewable energy used.
To conclude, a strong advocacy is made on the need to put in place stiffer global institutions and policies that enforce conventions and laws on the reduction of carbon emission. Existing institutions and mechanisms have only seems to be white elephants and toothless bull dogs who do virtually nothing to offenders. In fact, the time has come to change the trend. The time has indeed come give the institutions more power to sanction offenders. It is also important to have pragmatic research institutions who would continue to proof the usefulness of switching to renewable energy sources. Indeed, if countries are being punished today for using nuclear weapons, the time should also come for countries to be punished for excessive emission of carbon dioxide.
REFERENCE
Earth Trends. Carbon Emissions of Selected Countries. 2011. Web. January 30, 2012
Europe’s Energy Portal. Overview of European Union Energy Situation. 2011. Web. January 30, 2012
Read
More
sponsored ads
Save Your Time for More Important Things
Let us write or edit the case study on your topic
"Energy Sustainability Calculations"
with a personal 20% discount.
GRAB THE BEST PAPER

✕
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY